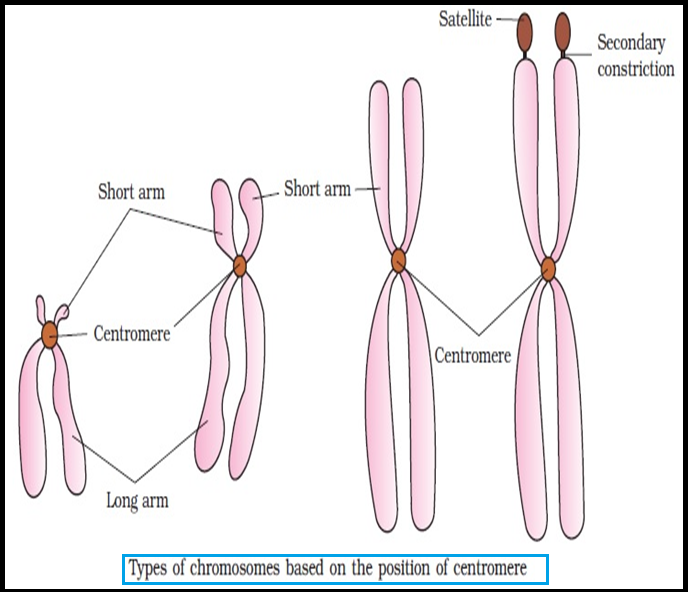
NUCLEUS
● `color{Brown}"Nucleus"` as a cell organelle was first described by `color{Brown}"Robert Brown"` as early as `color{violet}"1831"`.
● Later the material of the nucleus stained by the `color{violet}"basic dyes"` was given the name `color{Brown}"chromatin"` by `color{Brown}"Flemming"`.
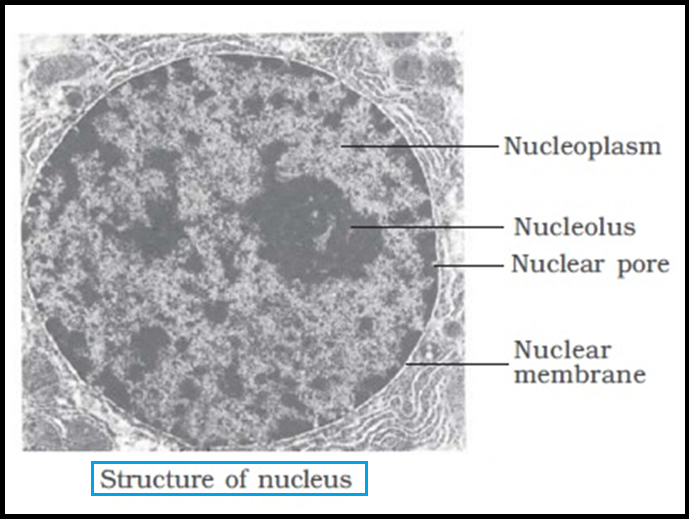
● The `color{Brown}"interphase nucleus"` (nucleus of a cell when it is not dividing) has highly extended and elaborate `color{violet}"nucleoprotein fibres"` called `color{Brown}"chromatin"`, nuclear matrix and one or more spherical bodies called `color{Brown}"nucleoli"` (sing.: nucleolus).
● `color{violet}"Electron microscopy"` has revealed that the `color{Brown}"nuclear envelope"`, which consists of two parallel membranes with a space between `color{violet}"(10 to 50 nm)"` called the `color{Brown}"perinuclear space"`, forms a barrier between the materials present inside the nucleus and that of the cytoplasm.
● The `color{violet}"outer membrane"` usually remains continuous with the `color{violet}"endoplasmic reticulum"` and also bears `color{violet}"ribosomes"` on it.
● At a number of places the `color{violet}"nuclear envelope"` is interrupted by `color{Brown}"minute pores"`, which are formed by the `color{violet}"fusion"` of its two membranes.
● These `color{violet}"nuclear pores"` are the `color{violet}"passages"` through which `color{violet}"movement of RNA and protein"` molecules takes place in `color{violet}"both directions"` between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
● Normally, there is only `color{violet}"one nucleus per cell,"` variations in the number of nuclei are also `color{violet}"frequently observed"`.
● Some mature cells even `color{violet}"lack nucleus"`, e.g., `color{brown}"erythrocytes of many mammals"` and `color{brown}"sieve tube cells"` of vascular plants.
● The `color{violet}"nuclear matrix"` or the `color{Brown}"nucleoplasm"` contains `color{violet}"nucleolus and chromatin"`.
● The `color{Brown}"nucleoli"` are `color{violet}"spherical structures"` present in the `color{violet}"nucleoplasm"`.
● The content of nucleolus is `color{violet}"continuous"` with the rest of the nucleoplasm as it is `color{violet}"not a membrane bound"` structure.
● It is a site for `color{violet}"active ribosomal RNA synthesis"`.
● `color{violet}"Larger and more numerous"` nucleoli are present in cells actively carrying out `color{violet}"protein synthesi"`s.
● Later the material of the nucleus stained by the `color{violet}"basic dyes"` was given the name `color{Brown}"chromatin"` by `color{Brown}"Flemming"`.
● The `color{Brown}"interphase nucleus"` (nucleus of a cell when it is not dividing) has highly extended and elaborate `color{violet}"nucleoprotein fibres"` called `color{Brown}"chromatin"`, nuclear matrix and one or more spherical bodies called `color{Brown}"nucleoli"` (sing.: nucleolus).
● `color{violet}"Electron microscopy"` has revealed that the `color{Brown}"nuclear envelope"`, which consists of two parallel membranes with a space between `color{violet}"(10 to 50 nm)"` called the `color{Brown}"perinuclear space"`, forms a barrier between the materials present inside the nucleus and that of the cytoplasm.
● The `color{violet}"outer membrane"` usually remains continuous with the `color{violet}"endoplasmic reticulum"` and also bears `color{violet}"ribosomes"` on it.
● At a number of places the `color{violet}"nuclear envelope"` is interrupted by `color{Brown}"minute pores"`, which are formed by the `color{violet}"fusion"` of its two membranes.
● These `color{violet}"nuclear pores"` are the `color{violet}"passages"` through which `color{violet}"movement of RNA and protein"` molecules takes place in `color{violet}"both directions"` between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
● Normally, there is only `color{violet}"one nucleus per cell,"` variations in the number of nuclei are also `color{violet}"frequently observed"`.
● Some mature cells even `color{violet}"lack nucleus"`, e.g., `color{brown}"erythrocytes of many mammals"` and `color{brown}"sieve tube cells"` of vascular plants.
● The `color{violet}"nuclear matrix"` or the `color{Brown}"nucleoplasm"` contains `color{violet}"nucleolus and chromatin"`.
● The `color{Brown}"nucleoli"` are `color{violet}"spherical structures"` present in the `color{violet}"nucleoplasm"`.
● The content of nucleolus is `color{violet}"continuous"` with the rest of the nucleoplasm as it is `color{violet}"not a membrane bound"` structure.
● It is a site for `color{violet}"active ribosomal RNA synthesis"`.
● `color{violet}"Larger and more numerous"` nucleoli are present in cells actively carrying out `color{violet}"protein synthesi"`s.